|
Multifunctional Sport Hall Engineer: Zsolt Nagy Design office: Gordias Srl. www.gordias.ro Location: Cluj-Napoca, Romania Size: 93 X 76 X 27 m Members: 2773 Material: S275, C25 Weight: 352 t |
get your personal quote: sales@ergocad.eu |
|
The csJoint connection design software can be run as a stand-alone application and has proved to be an efficient tool for structural connection design. The main features are shown below:
|
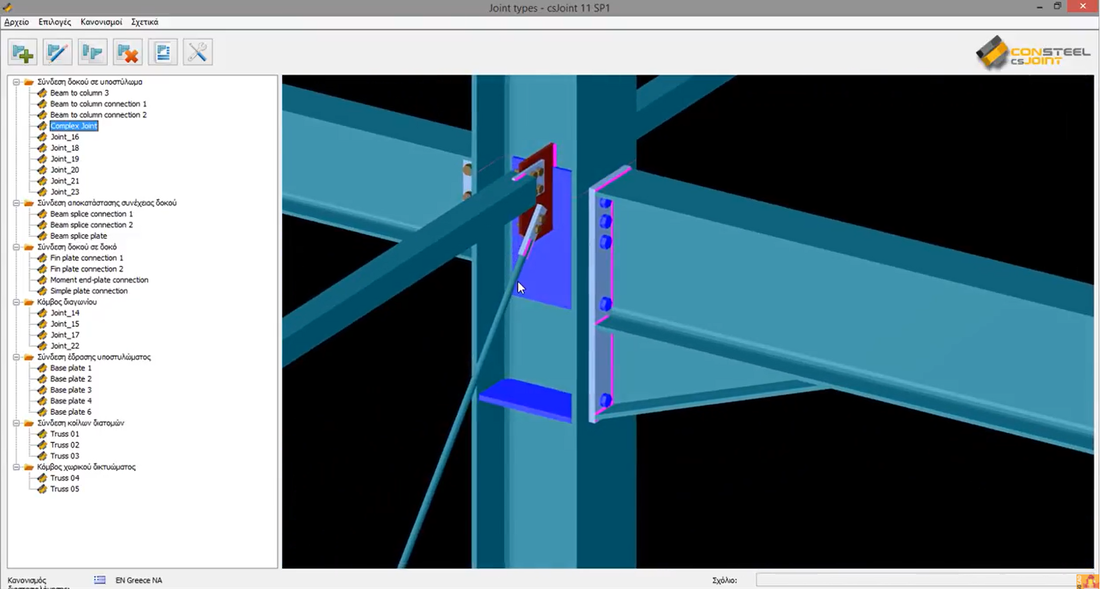
A great range of different joint types can be created easily applying several special connection elements, the design tools covers practically the whole joint standard Eurocode 3 Part 1-8.
A joint can be defined alone or based on the global model by the automatic joint identification tool. A prepared joint can be placed several parts of the global model to make the joint integral part of it. A placed joint is always rechecked automatically based on the current analysis results, and the connection stiffness is also updated modifying the global model consequently. |
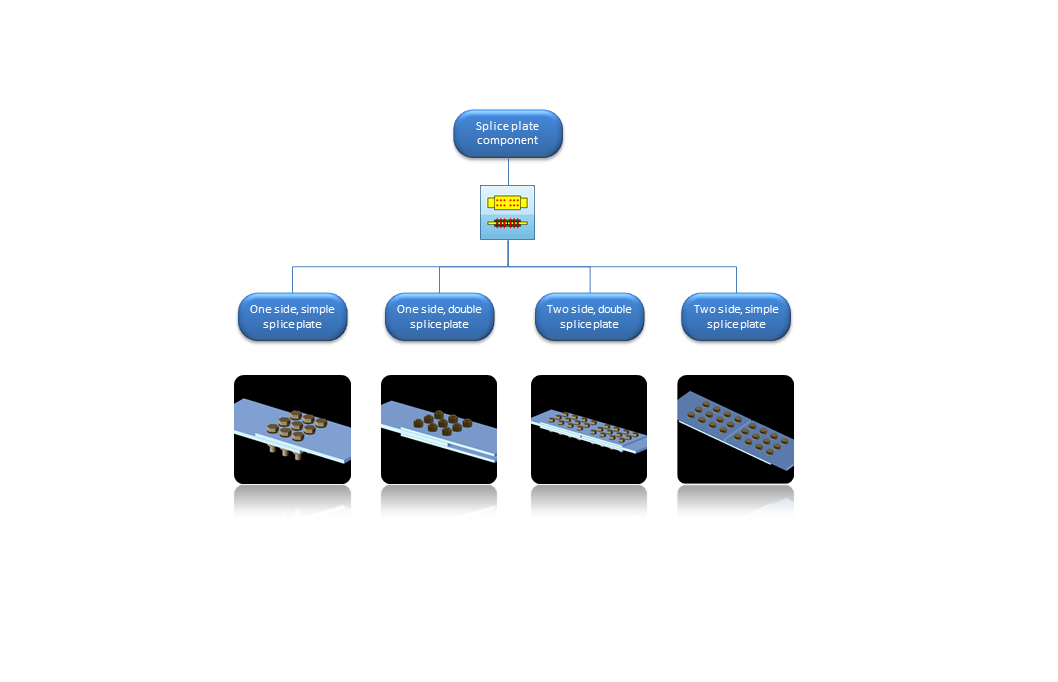
Joint types
The number of the joint types is one of the most dynamically developing parts of the software, usually considering the claims of the users.
At the moment the csJoint module has the following joint and connection types:
At the moment the csJoint module has the following joint and connection types:
|
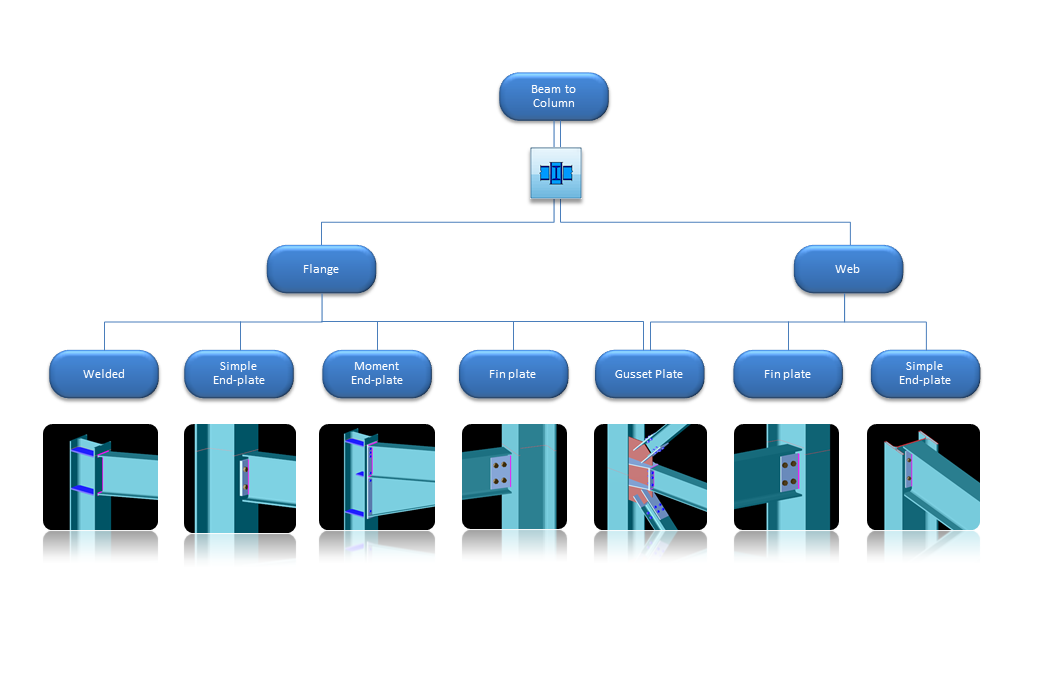
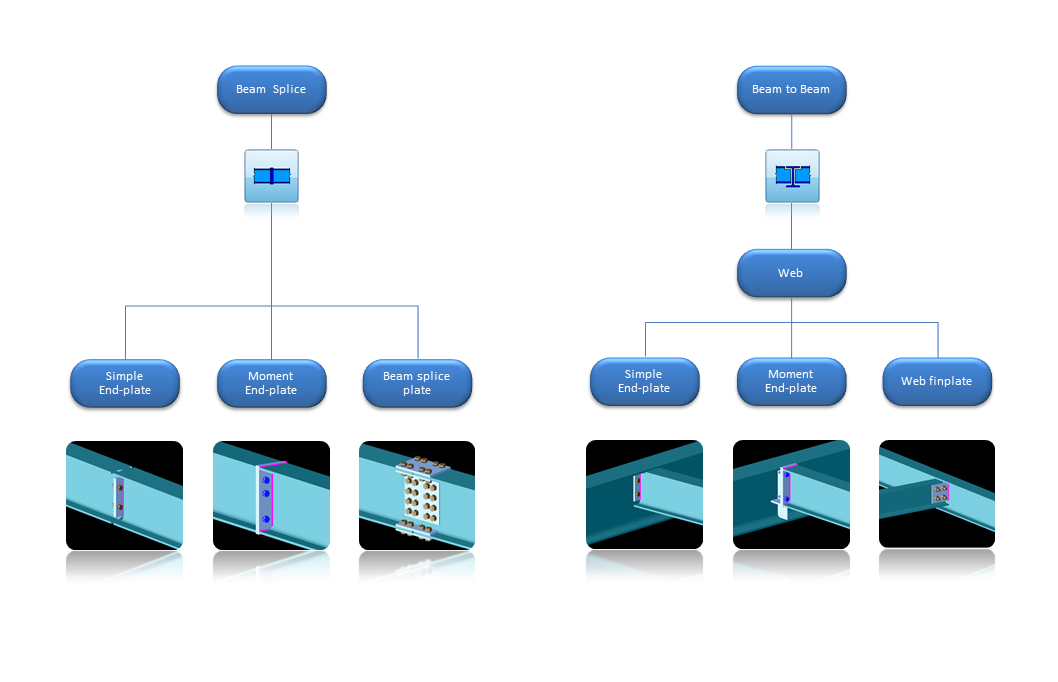
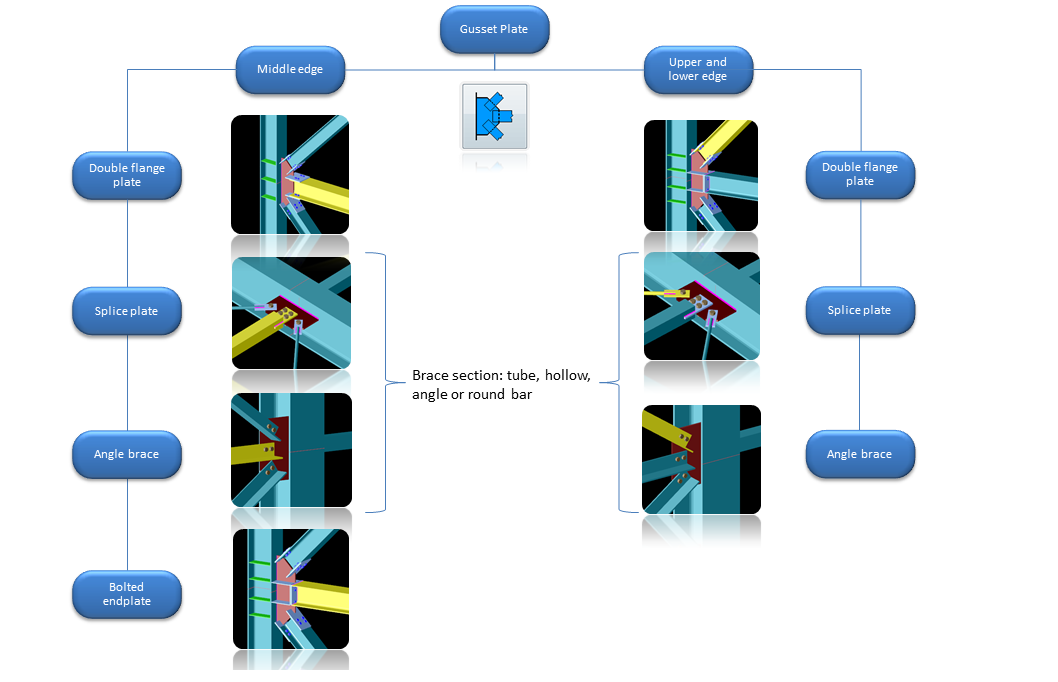
Beam-to-column joints with
|
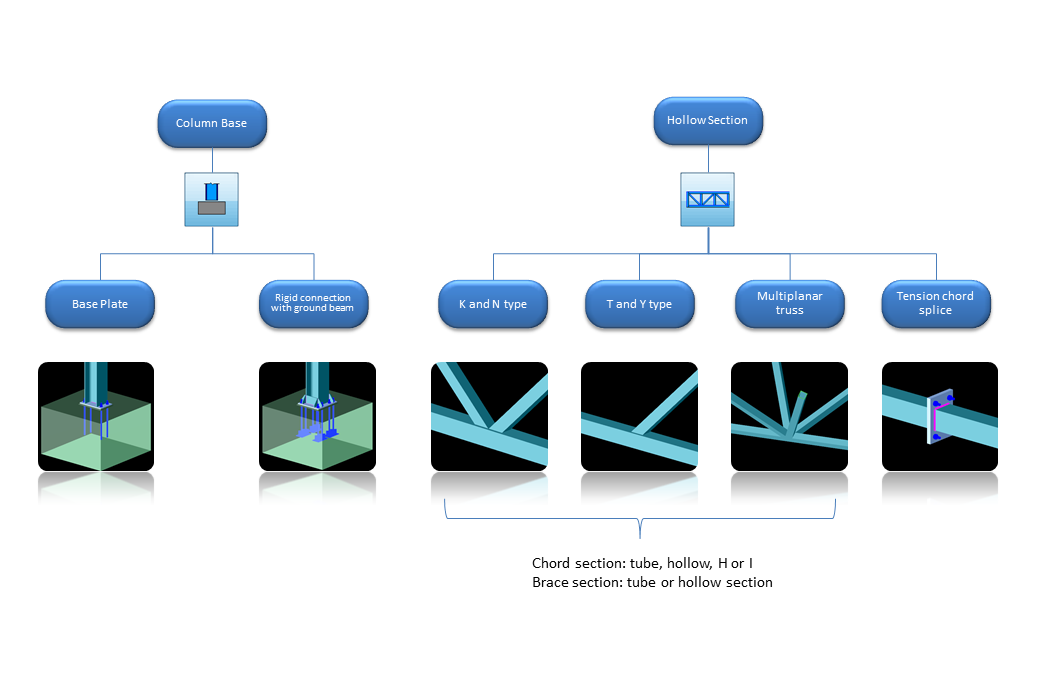
Column base joints with
|
The module offers a number of strengthening possibilities such as: lower and/or upper haunch with or without flange, transverse web stiffeners, flange stiffeners and flange backing plates, shear stiffeners (supplementary web plate, Morrison stiffener, single or double skew plate stiffener) etc.
Interaction
The most up-to-date structural design procedures take into account the mechanical interaction between the global structural model and its connections (rigid, semi-rigid or pinned) which generally makes the results more economic and realistic. However this approach requires a more complicated relationship between the joints and the structure and accordingly more serious modeling efforts from the engineer.
|
Structure-joint interaction
In ConSteel all the joint types can be defined freely or based on the global model geometry using the automatic identification tool, which examines the position of the connected members and the proper cross-sections and offer the possible joint types. After defining the joint it can be placed back to the global model and the appropriate connection stiffness can be automatically used in the global analysis, and a placed joint is always rechecked based on the current analysis results.
|
|
Analysis of connections
All the analyses in the csJoint module are based on the standard procedures of Eurocode 3 Part 1-8. These procedures are almost entirely covered by the module. For the different types of connections the following analyses are performed:
Moment connections:
|
|
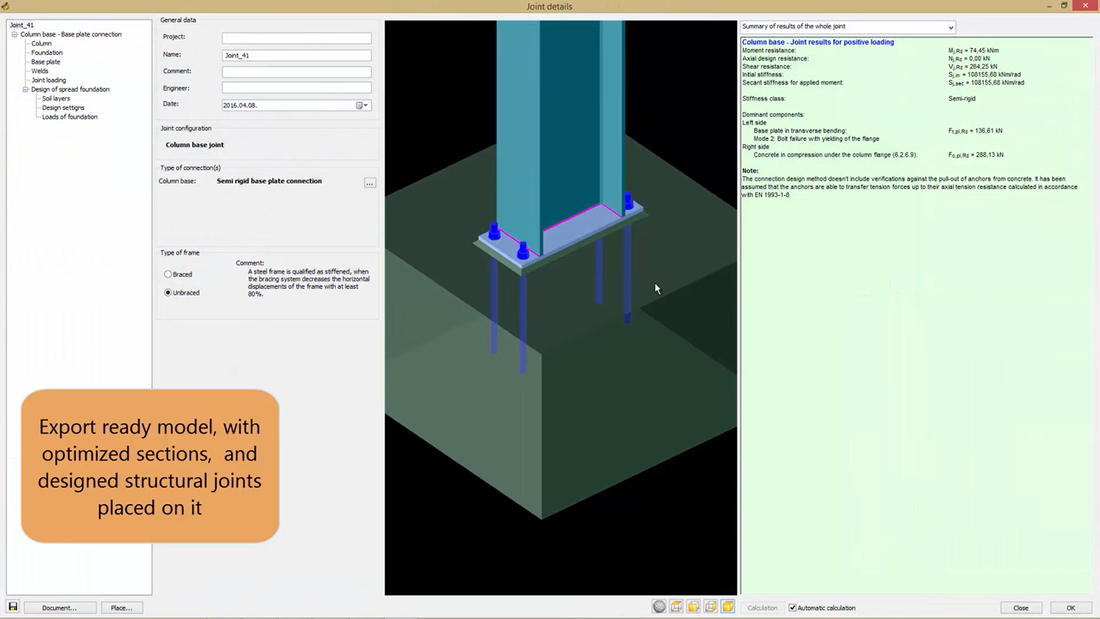
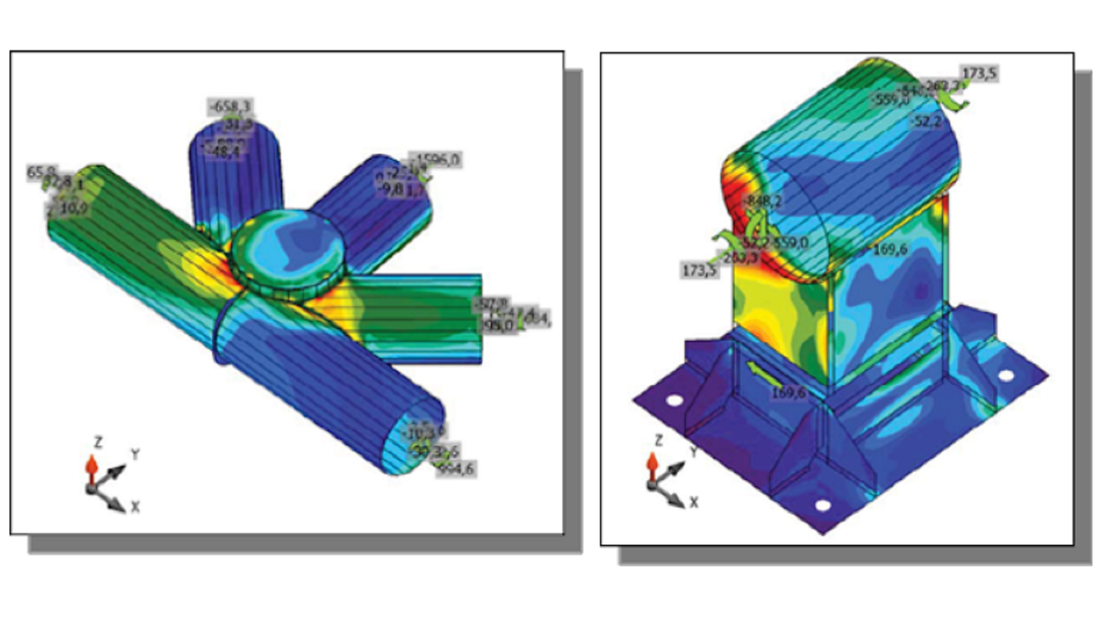
Results and documentation
The analysis results are displayed in two main forms: a summarized view containing the main resistances, stiffness and capacities; and a detailed view showing the components of the main results which is comprehensive enough to see what are the weakest points of the connections and what type of strengthening would be the most efficient to apply. A joint is calculated for all the loads coming from different places or different combinations, and the dominant place and combination is automatically highlighted. The spectacular documentation shows the detailed geometry of the joint with its connections, and the summarized and detailed results for all cases can be flexibly documented.
|
|
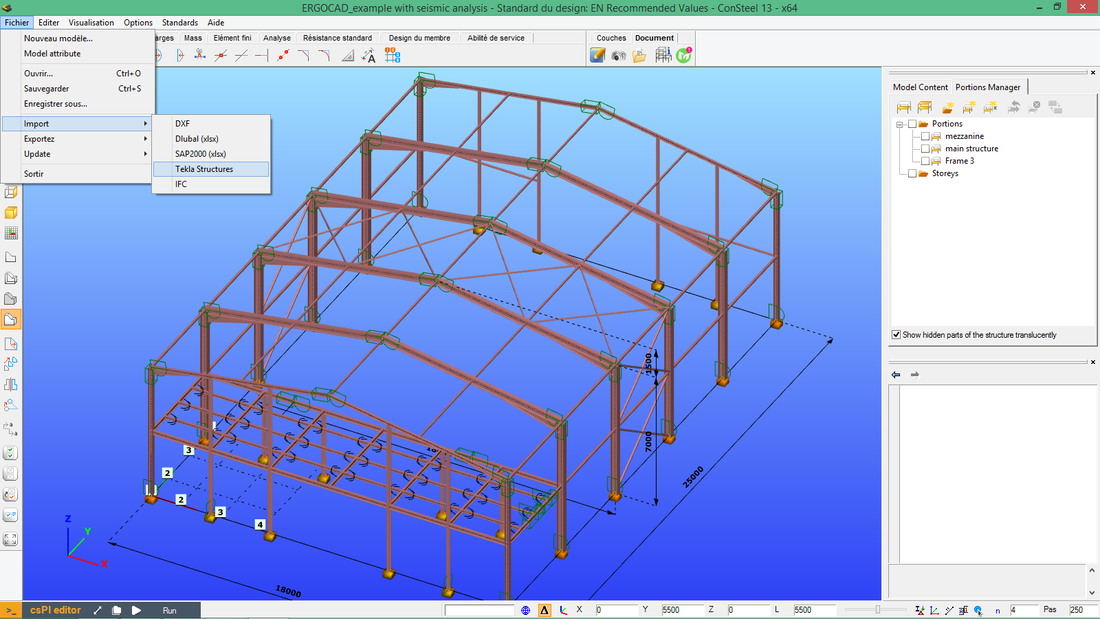
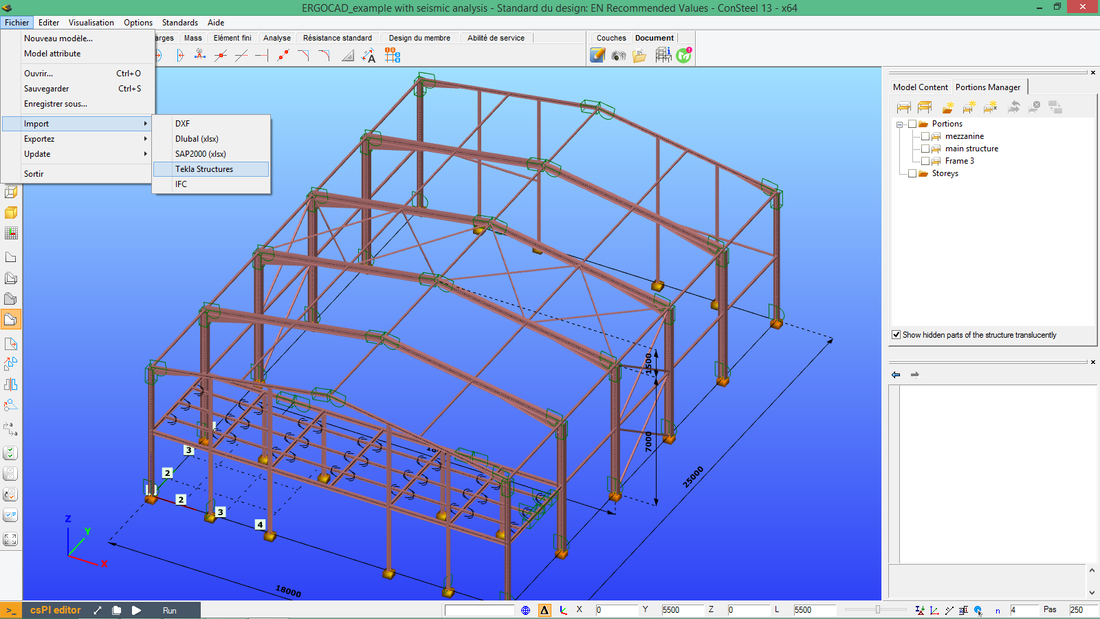
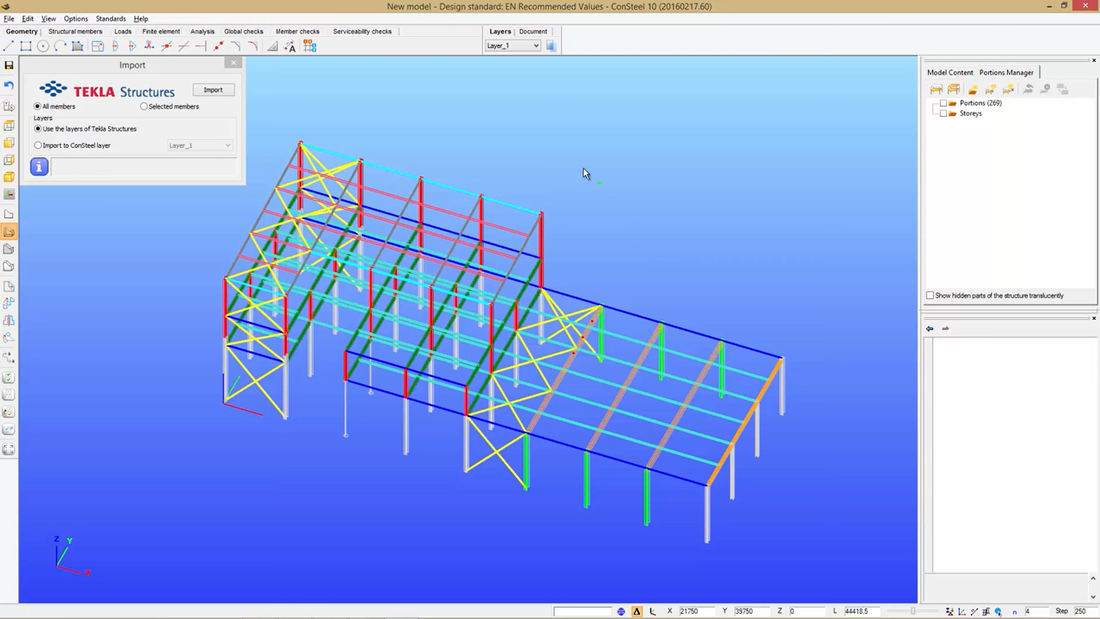
Direct model export to Tekla Structures & StruCad
The joint models appearing in ConSteel have the corresponding joint detailing macro, so the designed structural model with the placed joint models can easily be converted in one piece into the detailing model without additional drawing efforts on the joints.
|
|
Bidirectional link between ConSteel & IDEA Statica
Thanks to the high-level link between ConSteel and IDEA StatiCa, joints were identified and created based on the ConSteel structural model. Not just the geometry, but the loadings from all of the relevant structural points were transferred to IDEA StatiCa. In case of any modification, ConSteel automatically updated the IDEA connection models.
|